Real Patient Findings with simonONE: A Year in Review
With nearly 700 scans done in 2022, simonONE scans detected previously unknown cancers, cerebrovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and more in our patients. By offering advanced and affordable medical imaging, our patients now have a better understanding of their bodies to receive life-saving medical treatments, and for overall better health and wellness in the future.
We are sharing 10 real patient stories and imaging findings to demonstrate what simonONE can offer you, and how it can significantly impact your life.
- Cerebrovascular disease
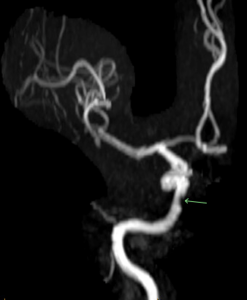
Narrowing of the precavernous carotid artery by 50% due to plaque buildup was noted on this patient’s MRA. MR angiography (MRA) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate your body’s blood vessels. The common carotid artery begins in the neck, continues into the skull and eventually joins with the Circle of Willis. The Circle of Willis is a ring of several arteries that supplies blood to the brain. Narrowing within the cerebral arteries can lead to an ischemic stroke. Medical and surgical management as well as lifestyle modifications to reduce stroke risk was discussed with the patient.
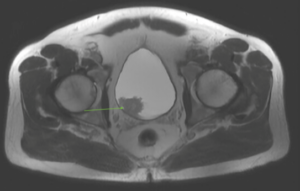
- Renal cell carcinoma
A >4 cm solid mass in the kidney that was later confirmed to be renal cell carcinoma was detected in our simonONE patient. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) rarely presents with symptoms until later in the disease process. The most common symptoms include blood in the urine, flank pain, weight loss, high blood pressure, and night sweats. The greatest risk factors for RCC are lifestyle-related factors such as smoking, obesity, high blood pressure and chronic kidney disease. Genetic factors also increase the risk of developing RCC, especially when involving immediate relatives. Detecting cancer in earlier stages greatly improves health outcomes and survivability.
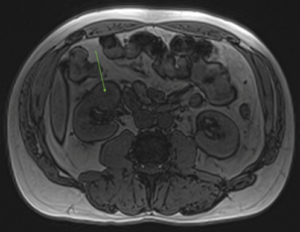
- Aortic aneurysm
An ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm measuring >4 cm was discovered. The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the body and is responsible for transporting oxygenated blood to our vital organs. An enlarged aorta, or an aortic aneurysm, occurs when the vessel wall weakens. Weakened vessels have a higher risk of tearing or rupture, and can lead to massive internal bleeding. It is important to detect, monitor, and manage an enlarged aorta to prevent life-threatening complications.
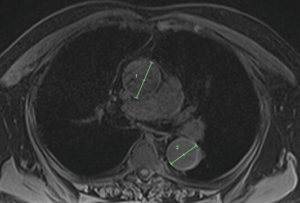
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) detected on the simonONE scan of a young patient. PKD is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within the kidneys, causing the kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. In the United States, PKD is the fourth leading cause of kidney failure. Most people do not develop symptoms until they are 30 to 40 years old, with high blood pressure as the most common sign of PKD. Untreated hypertension can further damage the kidneys over time.
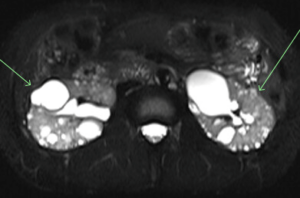
- Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
A >5 mm intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) was discovered in a patient with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. An IPMN is a type of growth within the pancreas that has the potential to develop into cancer over time. IPMN may grow in the main or side branch pancreatic ducts. A main-duct IPMN has approximately a 70% chance of developing malignancy. The radiologist recommended imaging surveillance and a referral to a gastroenterologist.
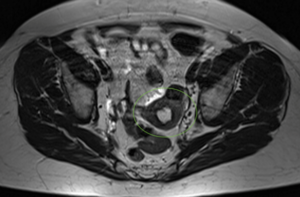
- Endometrial thickening
A thickened endometrial stripe >12 mm was found in a post-menopausal patient. Endometrial thickness after menopause may indicate malignancy when it is more than 4 to 5 mm thick. Endometrial cancer is the sixth most common cancer in women worldwide but is highly curable when found early.
- Cerebral aneurysm
A basilar tip aneurysm measuring 3 mm was detected. The basilar artery is a blood vessel that is formed from the union of two vertebral arteries. The vessel supplies blood to the cerebellum, brainstem and the posterior brain regions. Basilar tip aneurysms account for nearly 8% of all intracranial aneurysms. They are known to rupture more frequently than aneurysms in other locations, and treatment remains challenging. Early detection, surveillance, and intervention reduces the risk of suffering a hemorrhagic stroke.
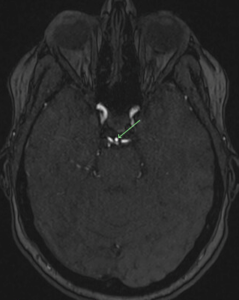
- Hippocampal volume loss
A NeuroQuant performed on a patient in their 60’s showed an abnormal hippocampal volume compared against age and gender matched controls. The hippocampus and the parietal lobe are the main areas of the brain that can indicate the potential for Alzheimer’s disease or dementia. Patients who have a smaller hippocampus are four times more likely to progress to Alzheimer’s disease in a few years than patients whose hippocampus is of a normal size. The hippocampus in a healthy older patient shrinks about 1% per year, compared to about 5% per year in a person with Alzheimer’s disease.
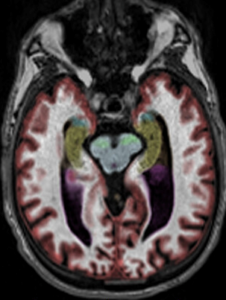
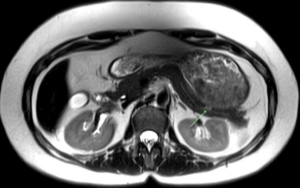
- Pancreatic cancer
A mass within the body of the pancreas highly concerning for pancreatic malignancy with metastasis to adjacent structures was detected in this simonONE scan. The average lifetime risk of pancreatic cancer is about 1 in 64, and it is slightly more common in men than women. Pancreatic cancer accounts for about 3% of all cancers in the US and about 7% of all cancer deaths.
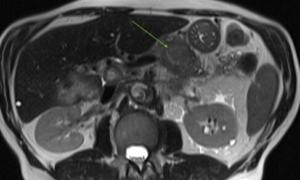
- Bladder cancer
A >2 cm bladder mass was detected in a simonONE patient experiencing abdominal pain and urinary symptoms. The mass was concerning for bladder cancer, and the radiologist recommended a follow-up with cystoscopy and biopsy for further evaluation. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men. Overall, the chance men will develop this cancer during their lifetime is about 1 in 28.